Microsoft surveyed 30,000 people in 31 different countries in 2021 as part of its Work Trend Index report, asking participants for their opinion on the most appropriate way to work and interact in a post-pandemic environment. 73% of respondents wanted to maintain flexible remote working options, but at the same time, 67% felt that face-to-face interaction was essential.
We are therefore faced with the dilemma of the new hybrid working model and its implications: it is now necessary to have options to connect from anywhere, at any time, using any device, synchronously or asynchronously, face-to-face or remotely, and also to provide an enriched user experience that even enhances collaboration in physical spaces. This substantially increases the complexity compared to previous paradigms, which were designed to try to emulate face-to-face scenarios in the workplace.
Companies must therefore adapt to this new situation, and it is here where tools that facilitate collaborative work play an essential role.
The market for CCUU solutions and collaboration
The consulting firm Omdia forecasts a global growth in users of collaboration tools that could reach 140 million by 2025, which translates into a business opportunity worth around 23 billion euros.
The technologies or tools that should serve to meet this demand are multiple and are part of a fragmented scenario, with the emergence of new players and solutions, as reflected in the Magic Quadrant (Meetings Solutions) published in 2021 by Gartner..
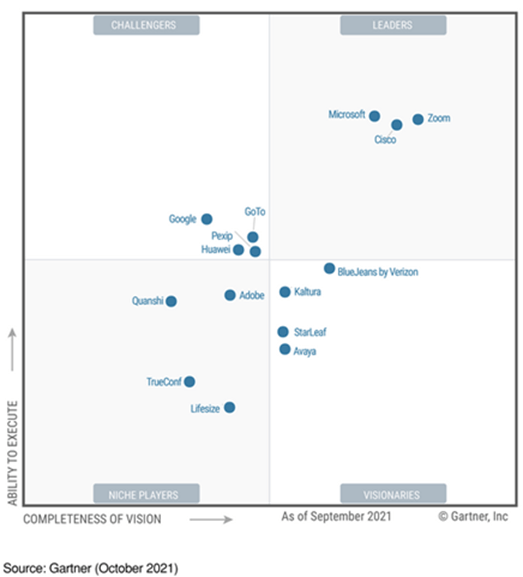
Cisco with Webex remains in the lead, although it shares this leadership with Microsoft Teams and Zoom, which have experienced significant growth in a very short period of time, threatening its dominant position:
- Microsoft Teams has become the de facto standard for collaborative work during the pandemic: the number of daily users before COVID-19, 20 million, has risen to 270 million active monthly users, according to one of the latest reports published by the company itself. The fact that Teams is part of the Office 365 office suite has undoubtedly been a key factor in facilitating its adoption, accelerated by the circumstances that the coronavirus imposed, suddenly demanding a global remote working environment. Teams has been the fastest growing business-oriented application in Microsoft’s history.
- Zoom has evolved from a cloud-based video conferencing offering to an end-to-end communications platform, building products ready for hybrid work environments. Its growth has also been exponential, reaching a market share of 28%. A freemium licensing model, supported by a simple and intuitive user experience that is easily adopted by the B2C segment, are part of the main reasons that have contributed to its rapid expansion.
Another trend in the Unified Communications market that Gartner highlights is the progressive migration towards cloud platforms as an alternative to in-house deployment. Gartner forecasts that by 2024, 3 out of every 4 user licenses will be linked to services deployed in the cloud.
Telefónica Tech expands its offer to meet the needs of any customer
Telefónica Tech, in constant adaptation to all these changes, proposes a catalogue of solutions with a double objective: to cover each of the use cases associated with hybrid work environments and to meet the needs of all types of customers.
The main characteristics of these solutions are:
- Adapted to the needs and typology of any company, guaranteeing a barrier-free user experience.
- Advanced and enriched with all the necessary functionality to ensure total collaboration between the different areas and teams of an organisation.
- Leaders, driven by alliances with the main partners in the market, through collaboration agreements and certifications that support a complete and qualitative proposal.
- Integrated with voice services, enhancing the user experience through a single interface for communication and collaboration.
- Complemented with professional services that allow us to adapt, implement and manage any type of customer requirement.
All of this translates into a series of specific actions:
- Constant expansion of the catalogue, offering the best ecosystem of solutions through strategic alliances with global leaders such as Cisco, Microsoft and Zoom.
- Applications always updated and enriched with the latest market innovations.
- Personalised advice with the aim of proposing the best solution for each client.
- Functionality complemented with value-added services, e.g. recorder, peripherals, etc.
- An economical pay-as-you-go model, avoiding costly up-front investments for the customer.
- A Global Operations and Support Centre is responsible for management and maintenance, providing all of Telefónica’s experience and knowledge in communications and collaboration solutions.
Five pillars of the best value proposition
Telefónica Tech’s value proposition, therefore, for collaboration products and services, is based on offering its customers a one-stop-shop experience, on cloud solutions, fully managed and adapted to their business requirements.
The main characteristics of this value proposition are:
- Customer centric: the satisfaction of customer needs as a priority objective, with a definition of profiles to meet the different use cases, including the best user experience.
- Complete offer: with a catalogue that includes an ecosystem made up of products from the main partners and manufacturers in the market, through strategic alliances, covering any functionality demand and aimed at all types of customers.
- Products always updated with the latest versions, offered as Software as a Service (SaaS) on cloud infrastructure.
- Scalable pay-per-use economic model, avoiding the need for costly initial investments.
- End-to-end managed service, including both initial advice to the client and the configuration, operation and advanced administration of the service.
Telefónica Tech is an industry leader in CCUU solutions and Collaboration
Telefónica Tech is a leader in Unified Communications solutions and Collaboration for companies. The activities carried out by its team of professionals complement the different technologies, thus enabling it to offer end-to-end services, with the aim of providing customers with the ability to isolate themselves from the complexity of these products and focus exclusively on their business.
Telefónica Tech’s main tasks include:
- Advice and planning: technical-economic analysis and proposal of the most appropriate solution.
- Design and implementation: implementation of the proposal made, based on the previous study.
- Migration: if necessary, of previous applications.