The homepage of the website features the claim that “Artists launch careers here” and with household names such as Imagine Dragons and Alabama Shakes starting their careers on this platform, this claim seems credible. ReverbNation is less of an agency and more of a social media platform (when an artist joins they can link their social media accounts to the site). The tools used to achieve exposure harness the power of Big Data. For example, the Crowd Review tool sends an artist’s song to a select group of music fans, who then provide feedback. The report for the artist features data driven analysis ranging from audience retention to commercial potential. ReverbNation also offers promotional tools, targeted fan interaction and website creation.
 |
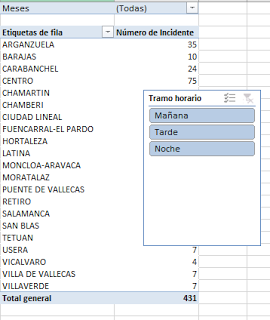
| Figure 1 : ReverbNation tools available to artists. |
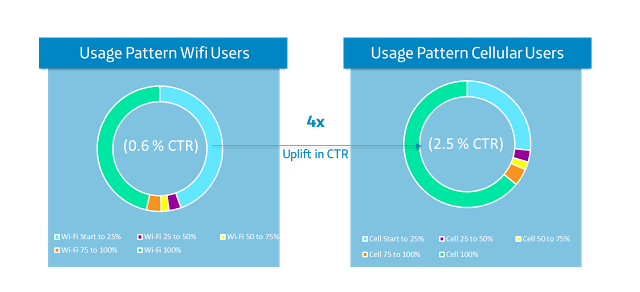
In our previous blog from March, it was shown how Big Data could cut out the intermediaries between label and artist in order to help artists financially. Now, ReverbNation is showing how data science can also bring efficiency to the process of finding the next best artist. The team at ReverbNation listen to artist uploads daily so still offer ‘human’ suggestions to labels based on what they hear. Additionally, labels and festival organizers alike can submit a request to the site and receive detailed statistics about artists’ music and marketability in order to make the perfect picks for their situation. For example, a rock festival in Paris could find an artist of that genre with a growing following in that region.
Artists have received festival slots at Bonnaroo and Ultra Music Festival
through ReverbNation.
 |
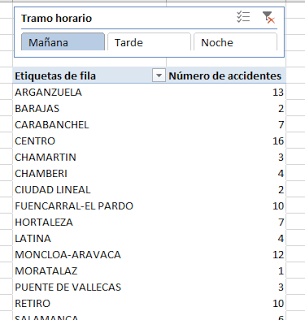
| Figure 2 : Spotify’s Discover feature. |
Of course, the thrill of stumbling across new music by chance will always exist. However, using the data available can bring efficiency to all areas of the music industry. The ‘lucky break’ that artists search for will involve less ‘luck’, and more data science. These processes can also be applied to other industries. For example, an art gallery could base their decision to showcase an artist’s work not on intuition, but on historic data of their performance. Here at LUCA, we are excited to see what Big Data can bring to the arts industries. What changes do you think we will see in the coming years?
Don’t miss out on a single post. Subscribe to LUCA Data Speaks.