 |
| Source: http://qz.com/79818/why-you-should-access-online-banking-on-your-smartphone-rather-than-your-computer/ |
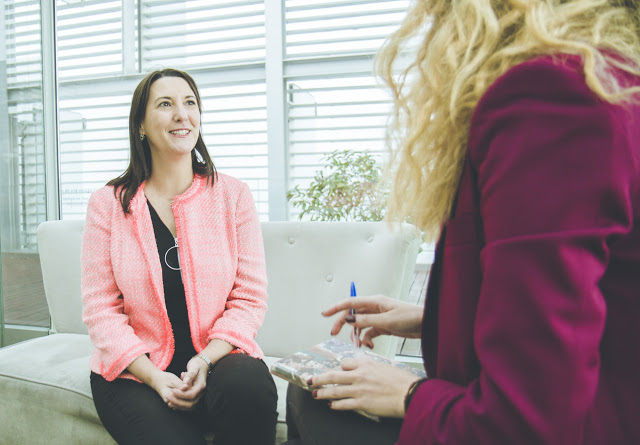
So far, we have seen applications which simulate to be an official application, necessary to operate with a bank from a mobile device. These are usually offered from fraudulent repositories or from the official store (during a short time, until it is detected). But there are other ways. Although not too many cases of this kind has been detected, malware previously hosted in the device could try to steal information from the legitimate bank application. For infecting the device in first place, the user has to install an application that contains malware or that “is” malware, although it may come from an email attachment, or even an infected PC. Then, it would be enough to get keystrokes or network data sent by the legitimate application.
Zeus could be purchased in black market for 2500-3000 €, providing a complete information arsenal for “learning to steal”. Aside, scammers may buy additional modules to improve funcionality or even use it as a service, renting infected botnets. In 2011 its source code was leaked, generating some other versions manteined by “the community”. SpyEye is a very popular banking trojan too, with quite a lot of plugins and advanced funcionality.
 |
| Source: https://blogs.rsa.com/is-cybercrime-ready-to-crown-a-new-kins-inth3wild/ |
Malware and phones
While security in online banking improves, integrating the cell phone as a second factor authentication, malware (specially Zeus and its variants) had to adapt and infect as well these devices. So, the term “MitMo” (Man in the mobile) was established for a kind of Zeus variant that tried to avoid online bank security by infecting smartphones as well and, obtaining in this way the SMS used for authentication. The user (with her PC already infected) is asked to download and execute an application for his smartphone. This malware for mobile devices has to work together with the trojan infecting the victim’s system. By themselves, they are not expected to specifically steal bank information while in the smartphone.
But new variants for Android have been spotted, specifically designed for stealing users from a particular bank. Alerted about a malware that, aside from stealing all kind of information from the smartphone itself, it is able to communicate via POST commands to a C&C server. But the most interesting feature is that it is specifically programmed to obtain the bank account balance for users registered with Sberbank Russian bank (sending a SMS to a free number available for their clients). It also intercepts every SMS and calls related to this bank. So this may be considered the first approach to a basic feature in PC banking trojans, that have been programmed long ago sepecifically for every bank.